Our skin is a canvas that tells the story of our lives, but sometimes, it reveals unwelcome marks in the form of hyperpigmentation and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). These skin conditions, though harmless, can impact our confidence and self-esteem. In this blog, we will delve into the world of hyperpigmentation and PIH, exploring their causes, differences, prevention, and effective treatment options.
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a skin condition characterized by the darkening or increased coloration of certain areas of the skin due to excessive production of melanin. Melanin is the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. When the body produces more melanin than usual or the pigment is unevenly distributed, it leads to the formation of dark patches or spots on the skin.
What is Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation?
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a skin condition characterized by the darkening of the skin in areas that have previously experienced inflammation or injury. It occurs as a result of an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of the skin, hair, and eyes. When the skin undergoes trauma or inflammation due to various factors like acne, eczema, psoriasis, burns, cuts, or other skin injuries, the body’s natural response is to produce more melanin in the affected area.
PIH typically appears as flat, dark patches or spots that can range in color from light brown to deep black, depending on the individual’s skin tone. These patches may be a few millimeters to several centimeters in size and can persist for weeks to months or even longer.
Role of SPF in the Treatment of Hyperpigmentation and PIH
The treatment for hyperpigmentation and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Regardless of the cause of hyperpigmentation or PIH, sun protection is crucial. UV rays can worsen pigmentation and darken existing spots. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily.
How to Fade Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
The post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation appears as small spots. As it appears after the skin breakout, it heals quickly. The skincare ingredients include salicylic acid, niacinamide, vitamin
C, AHA, or BHA are great to reduce PIH. You can try GTM MELA Cream with PDRN HA SERUM available at in store. It contains a powerful antioxidant and skin-brightening ingredient, Glutathione, Tranexamic Acid, Niacinamide, Medical HA; tyrosinase inhibitor. Tyrosinase is an enzyme involved in the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. By inhibiting tyrosinase activity, these ingredients helps regulate melanin production, which can lead to a reduction in hyperpigmentation. In addition, it prevents the development of post-inflammatory scars or dark spots.
Ingredients to Look for the Treatment of Hyperpigmentation and Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
When looking for skincare products to treat hyperpigmentation and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), it’s essential to seek ingredients with proven skin-brightening and pigment-reducing properties. Here are some effective ingredients to look for:
- Glutathione: A gold standard skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production and can effectively lighten dark spots. It is available in both over-the-counter and prescription-strength formulations.
- Tranexamic Acid: An amino acid that can help prevent the formation of pigmented spots and reduce the appearance of existing hyperpigmentation.
- Arbutin: A natural derivative of hydroquinone found in certain plants, arbutin can help brighten the skin and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids promote skin cell turnover and help fade hyperpigmentation over time. Look for products containing retinol, tretinoin, or other retinoid derivatives.
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid): A potent antioxidant that helps regulate melanin production, brighten the skin and reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation. Look for stable and well-formulated vitamin C serums.
- Niacinamide: Also known as vitamin B3, niacinamide can help reduce the appearance of dark spots and improve overall skin texture. It is well-tolerated by most skin types.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): AHAs, such as glycolic acid and lactic acid, exfoliate the skin’s surface, promoting the fading of hyperpigmentation and the renewal of healthy skin cells.
- Kojic Acid: A natural skin-lightening agent derived from fungi that can help reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
- Azelaic Acid: This ingredient has both exfoliating and pigment-reducing properties, making it effective for treating hyperpigmentation and PIH.
- Licorice Extract: Contains glabridin, which can help inhibit melanin production and lighten dark spots.
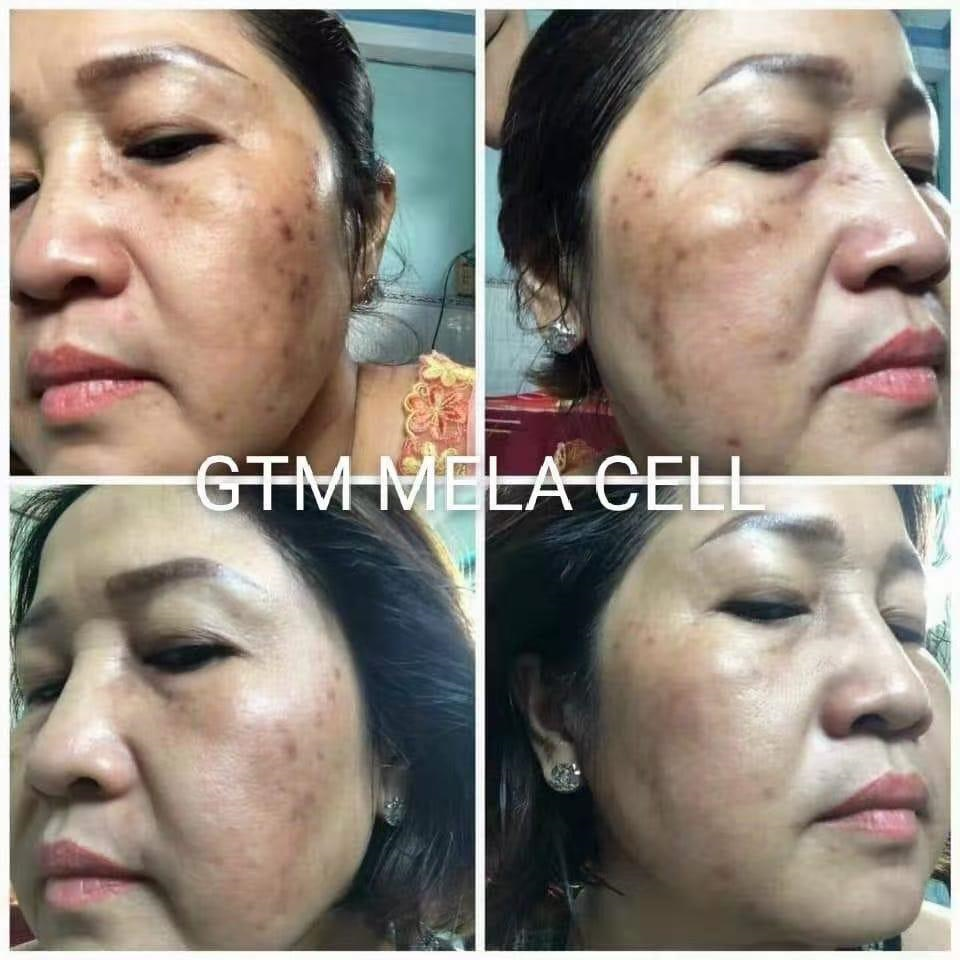
Try DEP Mela Cell + PDRN Skin Booster Treatment
The Mela Cell Treatment with PDRN and Transexamic acid is highly effective for the correction of hyperpigmentation. PDRN is a substance derived from the DNA of salmon or trout that has been used in various medical and aesthetic treatments. It is known for its regenerative properties and is believed to help stimulate tissue repair and collagen production. Its regenerative effects may contribute to skin renewal and potentially help with the fading of dark spots over time. By promoting collagen synthesis, PDRN can improve skin texture and overall complexion, which may have a positive impact on hyperpigmentation.
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine and is known for its antifibrinolytic properties. It is believed to work by inhibiting the activation of melanocytes and reducing the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. By limiting melanin production, tranexamic acid can help lighten dark spots and prevent the formation of new hyperpigmented areas.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, the treatment of hyperpigmentation and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) requires a multifaceted and patient approach. These conditions can be distressing, but with the right combination of treatments and proper skin care, significant improvement is achievable. Sun protection remains the cornerstone of any hyperpigmentation treatment plan, as it prevents further darkening and supports the efficacy of other treatments. Incorporating topical agents such as hydroquinone, retinoids, vitamin C, and niacinamide can help regulate melanin production and brighten the skin. Professional procedures like chemical peels and Mela Cell Treatment can also play a vital role in reducing hyperpigmentation. Additionally, for personalized and optimal results, it is crucial to consult a dermatologist who can tailor a treatment plan based on your skin type, severity of hyperpigmentation, and specific concerns. Remember, consistency, patience, and professional guidance are key to achieving a more even and radiant complexion, restoring your confidence, and helping you put your best face forward.